Bilateral Retinal Vasculopathy: Understanding Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Introduction:
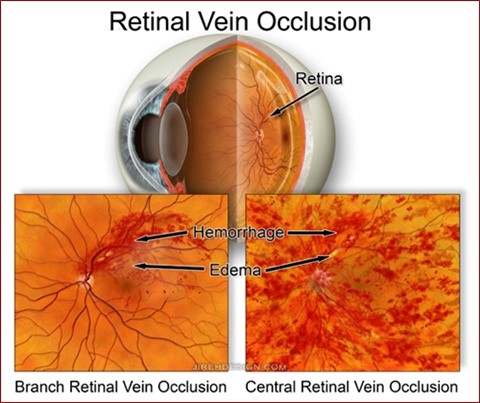
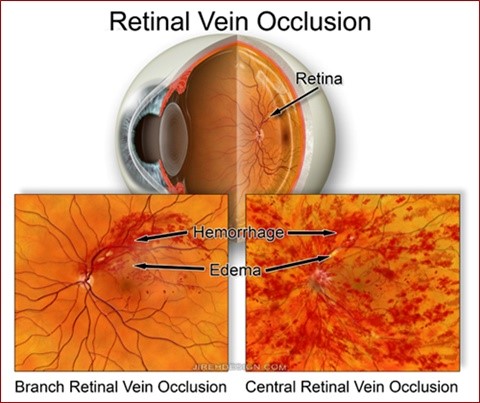
Bilateral retinal vasculopathy is a rare but serious eye condition that affects the blood vessels in the retina. This condition often results in decreased visual acuity, dilated and tortuous veins, white-centered retinal hemorrhages (Roth spots), and nonperfused areas. In this article, we will discuss the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of bilateral retinal vasculopathy.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of bilateral retinal vasculopathy include:
- Decreased visual acuity
- Dilated and tortuous veins
- White-centered retinal hemorrhages (Roth spots)
- Nonperfused areas
Bilateral retinal vasculopathy may also cause peripheral retinal vasculopathy with microaneurysms, which can be detected by fluorescein angiography. In some cases, patients may not exhibit any systemic symptoms, such as fever, increased heart rate, or fatigue.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis of bilateral retinal vasculopathy involves a comprehensive eye examination by an ophthalmologist who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of retinal diseases. The ophthalmologist will perform a dilated fundus examination, visual acuity test, and may use the fluorescein angiography to evaluate the retinal vasculature or other diagnostic tests. Medical and family history, along with physical examinations, should be taken in consideration as well. Timely diagnosis and management of this condition are crucial to prevent long-term complications and permanent vision loss.
Treatment:
The treatment for bilateral retinal vasculopathy depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. The sooner the condition is diagnosed, the better, as earlier diagnosis may help improve the outcome of treatments. The treatment options available for bilateral retinal vasculopathy include:
- Addressing the underlying medical condition (if present) that may be causing the vasculopathy.
- The use of Intravitreal therapy or intraocular injections of corticosteroids or other immune-suppressive agents in the management of macular edema and retinal inflammation.
- Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) agents, such as bevacizumab, ranibizumab, and aflibercept, for the treatment of neovascularization-proliferative retinopathy
- Laser photocoagulation can be helpful in cases where retinal bleeding or neovascularization is prominent.
- Surgical intervention, which is rarely done, such as vitrectomy (removal of the vitreous gel in the eye) and silicone oil tamponade in severe cases of retinal detachment.
Conclusion:
Patients who experience symptoms of bilateral retinal vasculopathy or other eye conditions should seek a professional eye examination immediately as early detection is critical to prevent long-term complications. With appropriate treatment and management, it is possible to slow down or halt the progression of the disease and retain useful vision.
keywords: Bilateral retinal vasculopathy, retinal diseases, vision loss, ophthalmology, diagnosis, treatment
Originally Post From https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaophthalmology/fullarticle/2819809?widget=personalizedcontent&previousarticle=2775577
Read more about this topic at
Retinal Vasculopathy with Cerebral Leukoencephalopathy …
Retinal Vasculopathy with Cerebral Leukoencephalopathy …