Thyroid Eye Disease Patients Maintain Improvement Two Years After Teprotumumab Infusions
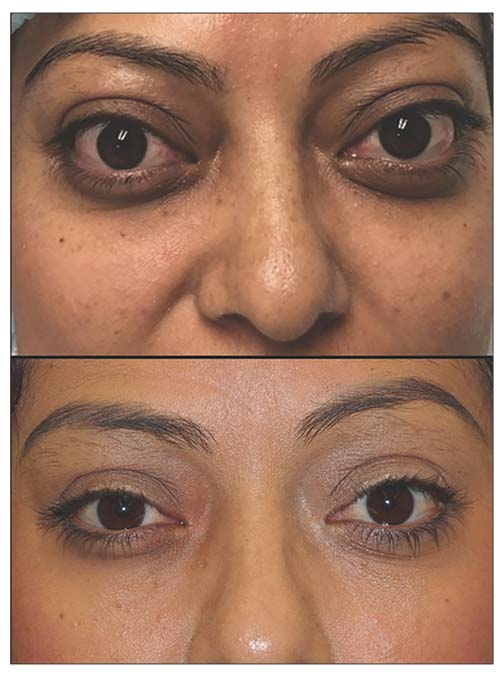
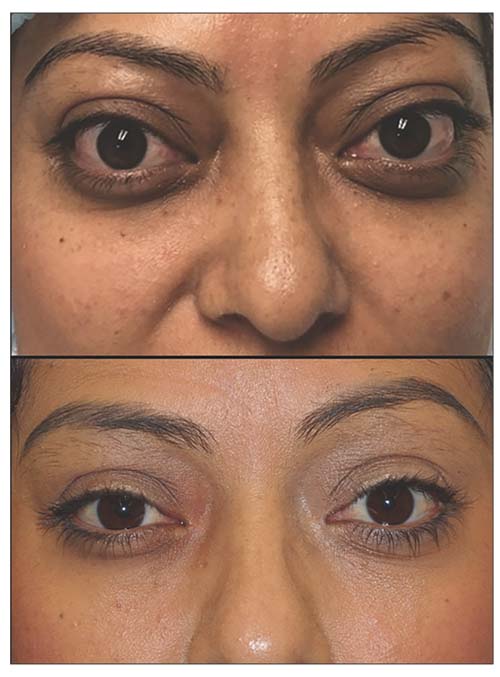
A recent industry-supported study presented at ENDO 2024 and published in the journal Thyroid shows that most patients with thyroid eye disease treated with teprotumumab usually don’t require additional treatments nearly two years later. Thyroid eye disease is an autoimmune disease that affects the tissues surrounding the eye and can cause eye bulging and double vision.
Why Teprotumumab Is Important for Thyroid Eye Disease Treatment
Thyroid eye disease is a lifelong condition that can worsen or flare up, regardless of treatment. So, it’s essential to understand whether patients treated with a full course of teprotumumab can experience lasting improvements in symptoms like eye bulging and double vision. To investigate this, researchers, including George Kahaly of Johannes Gutenberg University Medical Center, looked at the longer-term effects of teprotumumab treatment.
Long-Term Results of Teprotumumab Treatment for Thyroid Eye Disease
The researchers analyzed data beyond the 24-week treatment period for patients in the OPTIC and OPTIC-X studies who received a full eight-course of teprotumumab, up to week 72 (51 weeks post-last teprotumumab infusion). They investigated whether or not patients received additional therapy from week 24 through week 120 (99 weeks after therapy), as a measure of lasting benefit.
The study showed that patients who received teprotumumab maintained its efficacy for 51 weeks after the last infusion at week 72. Additionally, after nearly two years since the completion of the treatment period, 82% of patients didn’t need further treatment for thyroid eye disease. The remaining 18% (19/106) of reporting patients received additional medication like systemic steroids or teprotumumab and/or remedial periocular surgery 99 weeks post-therapy.
Implications for Physicians and Patients
As physicians consider the appropriate treatment approach for their thyroid eye disease patients, it’s essential to have longer-term data to support the use of teprotumumab in eligible patients. The study results offer a sigh of relief for patients with thyroid eye disease, providing adequate evidence that teprotumumab is an effective and efficient treatment option.
Conclusion
Patients with thyroid eye disease who received a full course of teprotumumab showed a sustained improvement in signs and symptoms like eye bulging and double vision. The study results provide evidence that teprotumumab is a reliable and efficient treatment option for eligible patients, ensuring longer-term results and saving them from further need for treatment.
Originally Post From https://medicalxpress.com/news/2024-05-thyroid-eye-disease-patients-years.html?deviceType=desktop